Using cryogenic electron microscopy to advance protein degradation research
What is Cryo-EM?
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is an advanced method of imaging small, complex and dynamic molecules, such as proteins.
Cryo-EM allows researchers to see the 3D details of protein structures and how proteins interact with one another at physiologic conditions (their natural environments within the body).

How does Cryo-EM work?
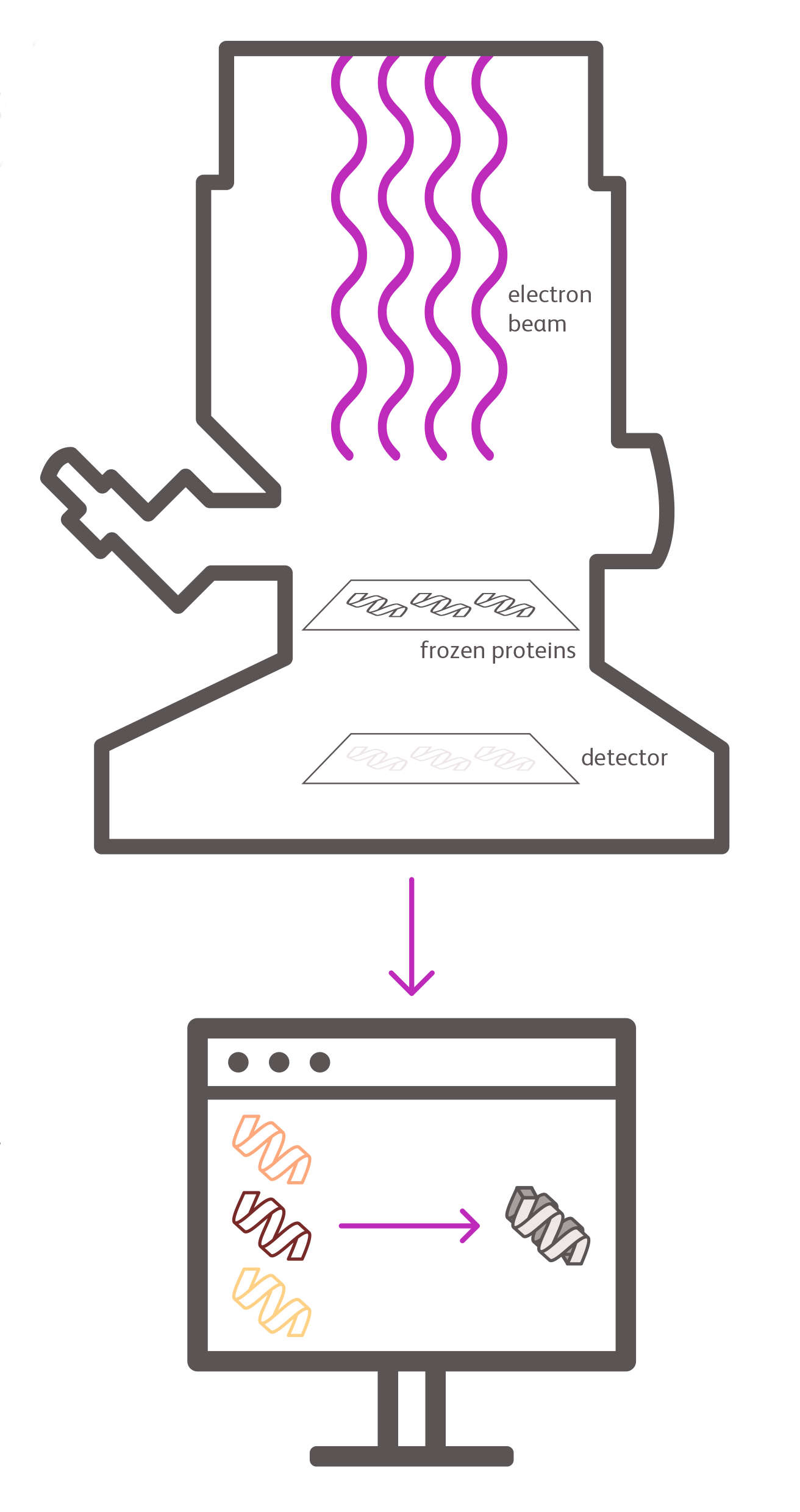
Cryo-EM uses a microscope that shoots beams of electrons at a sample at cryogenic conditions (extremely low temperatures).
 |
First, scientists will take the sample being examined and flash freeze it at extremely low temperatures. This "freezes" the molecules at a moment in time and allows scientists to examine them in their natural state and environment. |
 |
They will then place the sample inside the microscope and shoot a beam of electrons at it.
|
 |
A detector underneath the sample detects the electrons, creating images that are relayed to a computer. This process repeats over and over to capture thousands of angles and details of the sample. |
 |
The computer can then take these images produced by the microscope and combine them to create one 3D model of the entire molecule. |